They will be available under the ‘Resource’ tab on each session page.
How It Works
Mitacs is excited to provide professional development courses that respond to modern learning preferences, and better align our content with the competencies needed by industry partners and employers.

The courses are designed to complement the hands-on research skills and experience gained by participants of Mitacs programs (Accelerate, BSI, Elevate, Globalink) and Canadian college and university students. Each course is designed to improve upon one or more core competencies and is facilitated by industry leaders.
UPDATE: In February 2023 all 32 Mitacs asynchronous (online) courses will be WCAG 2.0 AA standards compliant that Mitacs participants can access directly via the EDGE platform.
Noteworthy accessibility improvements now built-in for a seamless learning experience with assistive technology include:
- Consistent structure, spacing, and headings
- Fully accessible colour contrast ratios- Including new visually accessible graphics and integrated alternative text
- Accessible learning materials and resources in Word and Excel
- Media content suite includes subtitles and transcripts
Program Details
About Mitacs Training
Since 2008, Mitacs has been offering professional development training to advanced degree graduates, supplementing their education and research experience with the tools necessary to succeed in today’s workforce. Each year, thousands participate in training courses to augment their university learning.
Now it’s your turn.
Details
Our courses and workshops revolve around eight course bundles, comprising eight online self-paced courses and seven online instructor-led workshops. The synchronous components (instructor-led workshops) are offered in an engaging and interactive learning environment, with small groups typically ranging from 10 to 24 participants.
Who are our facilitators ?
Workshops are facilitated by leading business and industry professionals who have undergone a competitive selection process. Our facilitators are subject matter experts in their respective fields and understand what it takes to succeed professionally. Facilitators deliver hands-on, engaging, and experiential learning.
Courses and workshops are offered at no charge to graduate students and postdoctoral fellows currently registered at Mitacs partner colleges and universities in Canada.
Competencies covered
Our curriculum is designed to build competencies in five key areas that are recognized as vital to professional success. Each course addresses one or more of the following competencies:
- Professional & career fundamentals
- Interpersonal skills
- Communication
- Leadership & management
- Intrapreneuralism
Benefits of the Mitacs Curriculum
- Flexibility: Participants have the freedom to learn at their own pace, accommodating participants in various time zones and those with diverse work schedules
- Accessibility: Learners with different learning styles, preferences, and time constraints can benefit from self-paced courses, promoting inclusivity. Enhanced accessibility with animations and subtitles to support learning.
- Networking Opportunities: Foster a sense of community through group discussions and activities in virtual instructor-led courses.
- Expert guidance: Certified experts lead courses, ensuring structured learning experiences and covering essential content.
- Interactive learning and Real-time feedback: Get personalized guidance from instructors, addressing questions on the spot for a dynamic learning experience.
- Increased employability: Continuously updated skills and knowledge make individuals more attractive to employers.
- Free access for: Canadian university students of all levels, Mitacs program participants and recent graduates
- Bilingual language options
- Certification: Upon successful completion of any of our professional development courses, a certificate will be awarded for the respective course bundle.
Professional Development
Mitacs’s professional development program is designed to support university and college students, as well as Mitacs program participants, as they complete their research projects, prepare for leadership roles in their industry, and enhance their employability in their respective fields.
Course bundles
Note: Each course bundle includes an interactive instructor-led workshop following an online self-paced course.
The themes include:
Career planning
Boost your career – Self-paced e-learning. Asynchronous course ~ 1hr – 1.5 hrs
Moving from academia to the business world is not always an easy transition. This course helps you identify and highlight your transferrable skills. This includes how best to present your skills and become adept at job search strategies and networking to better prepare you for a job in your field of expertise.
There are two self-paced online units in this course:
- Unit 01: Professional development plan
- Unit 02: Ready, set, get recruited
Learning outcomes:
- Identify transferable skills for a non-academic career path to include in your resume
- Explore non-academic career paths suited to your educational background
- Identify core skills and competencies that can be presented confidently in an interview
Upon completion of this course, you are invited to self-enroll and participate in a facilitated session.
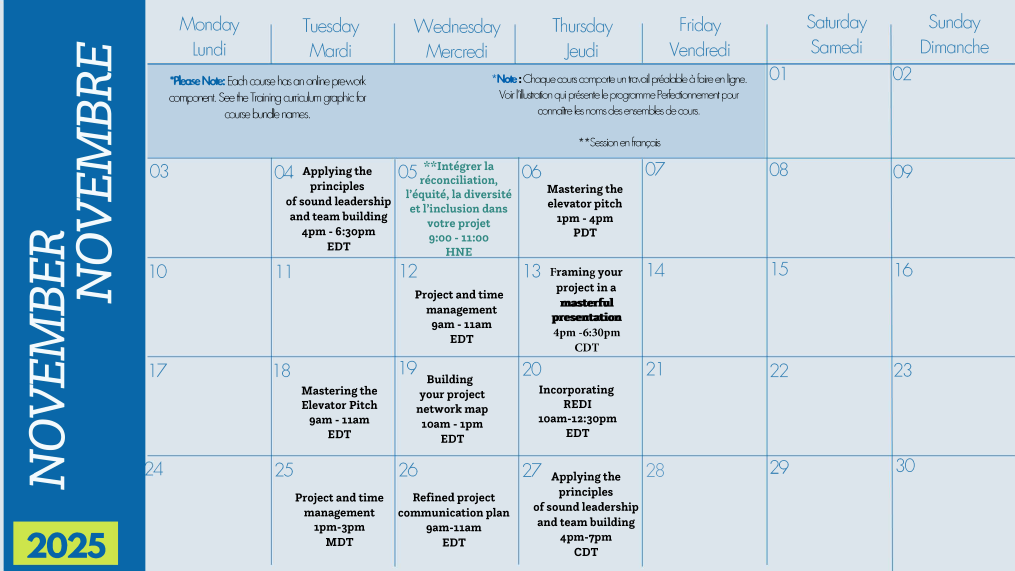
Mastering the elevator pitch – Facilitated workshop. Online ~ 2.5 – 3hrs
Craft a valuable plan for your goals in this course by developing your Individual Development Plan (IDP). Identify goals, competencies, interests, and strategies, creating a concrete plan to reach your aspirations.
In the facilitated session, participants share and receive feedback on their IDP drafts, refining plans through peer and facilitator input.
Learning objectives:
- Identify transferable skills for a non-academic career path
- Identify core skills and competencies for an interview
- Identify which of their core skills are transferrable among industries
Audience:
Learners that have completed the asynchronous course “Boost your career”.
Communication skills
Enhance your communication skills – Self-paced e-learning. Asynchronous course ~ 2 hrs
Effective communication is crucial in all aspects of life. This course helps you develop communication skills, especially in a private sector setting. Explore core elements and learn to shape project messaging, essential for audience engagement, gaining support, and securing partnerships and funding.
Learning outcomes:
- List the key elements of communications and how they impact the credibility of one’s communications
- Identify and create appropriate content tailored to the audience and purpose of your communications
- Summarize key points and explain complex concepts to specialists and non-specialists alike
- Describe the different expectations a research community may have for communication vs. a one-pager for a manager in a private company or not-for-profit organization
- Build out the communications plan for your project, including the unique value proposition
Upon completion of this course, you are invited to self-enroll and participate in a facilitated session.
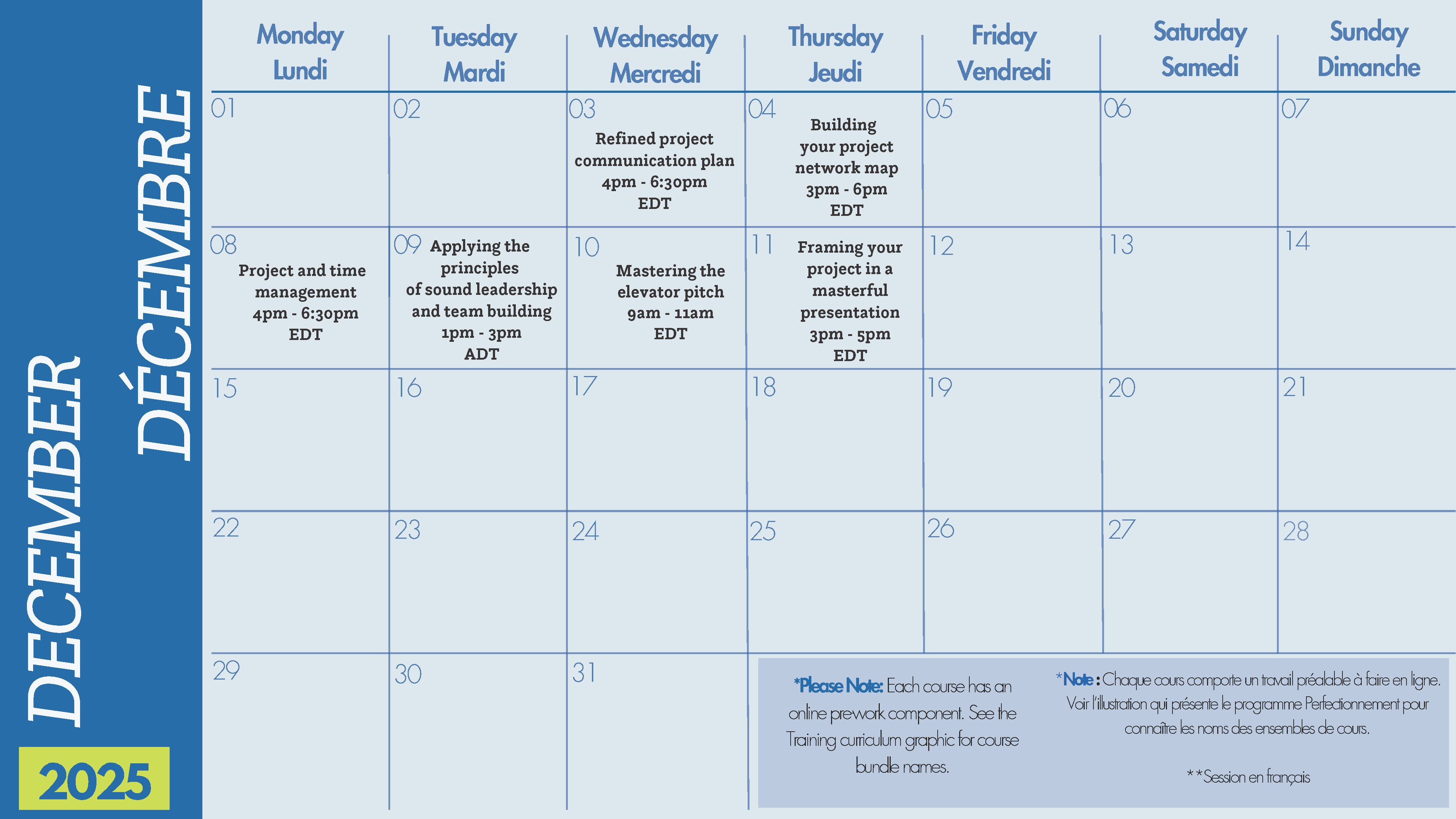
Refined project communication plan – Facilitated workshop. Online ~ 2 hrs – 3 hrs
Audience:
Learners that have completed the asynchronous course “Enhance your communication skills”.
Leadership skills
High-performing leadership and teams! – Self-paced e-learning. Asynchronous course ~ 1hr – 1.5 hrs
Leadership shapes a positive workplace culture. This course explores leadership’s significance across sectors, emphasizing its role in team dynamics and how effective leaders motivate and inspire employees.
Learning outcomes:
- Describe the qualities and skills of effective leaders today
- Explain leadership styles
- Describe how you can be a leader in your own organization, to support the business objectives
- List the characteristics of successful teams
- Explain how to ensure an inclusive workplace
- Identify burnout and stress
- Build on the interpersonal course by digging deeper into conflict management, avoidance, and progressive principles
Applying the principles of sound leadership and team building – Facilitated workshop. Online ~ 2 hrs
Management centers on execution, while leadership focuses on developing and empowering others. This course delves into effective leadership principles, exploring styles, traits, and issues affecting team dynamics and project outcomes. In a competitive world, effective leaders are vital for fostering strategic thinking, innovation, and action. In the facilitated session, build on foundational knowledge by identifying and critiquing leadership styles in demonstrated video scenarios.
Learning objectives:
- Describe the qualities of effective leaders
- Explain the various leadership styles
- Describe how you can be a leader in your own organization
- List the characteristics of successful teams
- Explain how to ensure an inclusive workplace
- Identify burnout and stress in your team
- Understand the details of conflict management and avoidance
Audience:
Learners that have completed the asynchronous course “High performing leadership and teams”.
Networking skills
Advance your reach – Self-paced e-learning. Asynchronous course ~ 1.5 hrs
Networking is crucial for career advancement, with many jobs secured through personal contacts. This course guides you in refining your online profile to establish meaningful connections, ensuring you’re well-positioned for success when a recruiter reaches out.
Learning outcomes:
- Have the skills to transition to a new role
- Set network goals
- Make your LinkedIn profile work for you
- Network with positive results
- Position yourself for a job in industry
Upon completion of this course, you are invited to self-enroll and participate in a facilitated session.
Building your project network map – Facilitated workshop. Online ~ 2hrs – 2.5 hrs
In a competitive market, being proactive in networking is vital. This interactive workshop will assist you in planning and constructing your project network map. Gain insights into strategies for organizing contacts, bridging gaps, and broadening your network. During the session, you’ll enhance your skills in creating a thorough project network map, pinpointing crucial decision-makers, influencers, funding sources, and users across all project stages, through collaborative brainstorming with your peers.
Learning objectives:
- Learn the skills to transition to a new role
- Set network goals
- Make your LinkedIn profile work for you
- How to network with positive results for your project and career
- How to position yourself for a job in industry
Audience:
Learners that have completed the asynchronous course “Advance your reach”.
Project and time management
Spur up your project management and time management skills – Self-paced e-learning. Asynchronous course ~ 1h-2hrs
Efficient time management reduces stress through organized task prioritization. This course teaches time and project management techniques to enhance performance. Evaluate personal challenges and learn to eliminate time-wasting behaviors for more effective time utilization.
Learning outcomes:
- Utilize time management strategies to be more effective and efficient on the job and when working remotely
- Describe different ways to manage email and use a calendar to schedule tasks
- Articulate the importance of managing stress to improve personal productivity
Upon completion of this course, you are invited to self-enroll and participate in a facilitated session.
Project and time management – Facilitated workshop. Online ~ 3hrs
Be intentional about your direction by adopting project and time management tools to guide your teams and work. In this course, practice using project status and update reports, along with a project plan, to organize, manage, and share your work. These skills enhance focus, alignment, and efficiency. The facilitated session allows you to practice delivering project status updates to stakeholders, presenting to small groups, and receiving peer feedback.
Learning objectives:
- Utilize time management strategies to be more effective when working remotely
- Manage email and calendar scheduling
- Articulate the importance of managing stress to improve productivity
- Understand the principles behind Waterfall and Agile project management
- Be able to complete a project charter, a project plan, and the Mitacs project costing template
Audience:
Learners that have completed the asynchronous course “Spur up your project management and time management skills”.
Reconciliation and EDI
Fostering a culture of reconciliation, equity, diversity, and inclusion – Self-paced e-learning. Asynchronous course ~ 1hr
Everyone contributes to enhancing equity, diversity, inclusion, and reconciliation. This course fosters essential ideas for a thriving professional community. Graduates, often assuming leadership roles, must be ready to apply the Truth and Reconciliation Commission’s 94 Calls to Action in their positions.
Learning outcomes:
- Explain why reconciliation and equity, diversity, and inclusion (REDI) actions are needed
- Articulate the concepts of reconciliation and EDI (REDI) in your workplaces
- Recognize situations where increased REDI is needed
- Describe how you can play a role in improving REDI
- Recognize and implement ways to break down cultural barriers and foster a diverse, inclusive workplace
Upon completion of this course, you are invited to self-enroll and participate in a facilitated session.
Incorporating REDI into your project – Facilitated workshop. Online ~ 2.5 – 3hrs
As a thought leader, prioritize equity, diversity, inclusion, and reconciliation efforts. This course offers an opportunity to reflect on and develop strategies for implementing REDI into your project, initiating powerful first steps towards systemic and behavioral changes. Identify reconciliation, equity, diversity, and inclusion (EDI) considerations for your project, discuss their incorporation into the project plan, and address these principles within the project team’s composition and methodology.
Learning objectives:
- Explain why reconciliation and equity, diversity, and inclusion are needed principles in professional and personal life
- Articulate the concepts behind reconciliation and EDI
- Recognize situations where increased reconciliation and EDI are needed
- Describe how you can play a role in improving reconciliation and EDI
- Recognize and implement ways to break down cultural barriers and foster a diverse, inclusive workplace
Audience:
Learners that have completed the asynchronous course “Fostering a culture of reconciliation, equity, diversity, and inclusion”.
R&D management
Research and development management – Self-paced e-learning. Asynchronous course ~ 2hrs
Having knowledge of business models and processes is fundamental to effective research and development management. This course looks at the fundamentals of business operations and explores the value of taking an intrapreneurship approach to business development.
There are three self-paced online units in this course:
- Unit 01: Understanding business
- Unit 02: Refining your proposal
- Unit 03: Entrepreneuralism
Learning outcomes:
- Describe how to read corporate financial reports such as a balance sheet and income statement
- Explain the value of business development and intrapreneurialism in the workplace
- Describe how to build a team for success
- Identify strategies to gather market intelligence
- Describe how to encourage, be part of, and deliver the entrepreneurial and intrapreneurial spirit in a large organization
Writing and presentation skills
Refine your writing and presentation skills – Self-paced e-learning. Asynchronous course ~ 1.5 hrs
As a technical expert, avoid overshooting your audience with complex language. This course refines your communication approach to effectively reach a broader audience. Building on the skills gained in the “Enhance your Communication Skills” course, which focused on strategic communication components, this course specifically delves into writing business reports, making presentations, and developing a pitch deck.
Learning outcomes:
- Differentiate between public sector (academic) and private and not-for-profit sector written materials
- Write a business report
- Identify and create appropriate content tailored to the audience and purpose of a presentation
- Structure your presentation
- Convey appropriate verbal and non-verbal communications techniques
- Develop a pitch deck for your Elevate project
- Demonstrate refined writing skills appropriate for the purpose of the document and the audience for whom it is intended
Upon completion of this course, you are invited to self-enroll and participate in a facilitated session.
Framing your project in a masterful presentation – Facilitated workshop. Online ~ 2 – 2.5 hrs
Master the art of delivering a successful pitch in just five minutes for your project, vision, or ideas with this course. Focusing on pitch fundamentals, development, delivery, and feedback, you’ll have ample opportunities to impress even the toughest audiences. In the facilitated session, craft a pitch presentation for your group (10 minutes, plus 5 minutes for Q&A), receiving valuable feedback from your peers.
Learning objectives:
- Differentiate between public and private sector writing
- How to write a business report
- Identify and create appropriate content tailored to the audience and purpose
- Structure your presentation
- Convey appropriate verbal and non-verbal communications
- Develop a pitch deck
- Demonstrate refined writing skills
Audience:
Learners that have completed the asynchronous course “Refine your writing and presentation skills”.
Register for Mitacs Training HERE
Specialized Training
 Announcing New Quantum Workshops
Announcing New Quantum Workshops
Are you prepared for the future of quantum? Qubo Consulting and Mitacs are thrilled to announce new quantum training sessions focused on developing Canadian talent to enter the quantum workforce. Come and explore quantum applications, meet quantum technology providers, or see a live quantum demonstration!
Our 3-hour online workshops give you a rare glimpse into the world of opportunities in the Quantum Industry—including a real-life quantum demonstration of the famous Young’s Double Slit Experiment. Participants will learn key opportunities, emerging risks and practical steps of how to stay competitive a quantum capabilities accelerate!
Quantum Workshops Schedule:
• Introduction to Quantum Technologies (Technical & Non-Technical) with Quantum Spotlight Guest Speaker Quantum Rings
When: January 14 at 2-5pm ET
• Quantum Sensing Use Cases (Technical) with Canadian Quantum Startup Spotlight Guest Speakers Qubic Technologies & Zero Point Cryogenics (ZPC)
When: January 28 at 2-5pm ET
• Quantum Computing Use Cases (Technical) with Quantum Spotlight Guest Speakers Aqarios & Canadian Quantum Startup Open Quantum Design (OQD)
When: February 11 at Time 11am-2pm ET
• The Quantum Space Race (Technical & Non-Technical) with Quantum Spotlight Guest Speaker Photonics Foundry
When: February 26 at Time 11am-2pm ET
• Quantum Communication Use Cases (Technical) with Canadian Quantum Startup Spotlight Guest Speaker Quantized Technologies Inc (QTi)
When: March 10 at 2-5pm ET
• Young’s Double Slit Demonstration & Workshop (Technical & Non-Technical)
When: March 24 at 2-5pm ET
Participants will receive a Certificate of Completion after each workshop. Register now!
NOTE: Limited spots available. The courses will be conducted in English with bilingual Q&A support. Non-technical audiences; suitable for everyone. Technical audiences; a STEM background (Science, Technology, Engineering & Math) is beneficial as content may move quickly.
**********

New AI Workshop Program Prepares Students for Industry-Ready Skills
Mitacs is excited to launch a new series of AI training workshops developed in partnership with the Concordia University Applied AI Institute. Beginning February 2025, this five-module program offers research students practical, industry-aligned skills in artificial intelligence, including foundational literacy, applied AI problem-solving, project management, and responsible AI practices.
Delivered by Concordia’s interdisciplinary network of AI experts, each 3-hour workshop blends interactive learning, real-world case studies, and hands-on skill development to help participants strengthen their career readiness and AI fluency.
AI Workshops Schedule:
-
AI Foundations for Industry-Ready Research Students – When: February 4, 2026, at 2pm ET
-
Applied AI Skills for Innovation Industry – When: February 18, 2026, at 2pm ET
-
AI Strategy and Project Management – When: March 4, 2026, at 2pm ET
-
Sustainable AI Practices: Balancing Innovation with Responsibility – When: March 18, 2026, at 2pm ET
-
AI & Career Toolkit for Mitacs Program Participants – When: March 31, 2026, at 2pm ET
All workshops will be opened to register two weeks prior to each session. Participants will receive a Certificate of Completion after each workshop. Register now to receive the latest information on the workshops!
Register HERE
NOTE: Limited spots available. The courses will be conducted in English.
Eligibility
Mitacs Training courses are available to all students and postdoctoral fellows at Mitacs partner colleges and universities in Canada, alumni who have graduated from a Canadian institution within the last two years, and current participants in Mitacs programs.
All parties involved with the Mitacs Training program must comply with the Canadian host institution’s policies regarding the ethical conduct of research and scholarly activities. Any issues or disputes around research or academic misconduct will be subject to the host institution’s processes following their institutional policies.
How to Apply
Register for Mitacs Training courses through the Mitacs EDGE portal for self-managed enrollment. Create an account on your first visit, secure your spot in instructor-led workshops with online registration, and receive a confirmation email.
Through EDGE (our Learning Management Platform), you will be able to:
- Access Mitacs Training’s online course catalog
- Register for workshops (For each bundled course, facilitated workshops are offered across Canada)
- View and download transcripts following successful course completion
- Check course registration status, download resources and tools, and more!
If you need to cancel a workshop, you have the option to unenroll and/or reschedule for another date. Cancellations are disabled five days before the course; for last-minute cancellations, contact [email protected].
To create an account, register and search for courses visit the EDGE portal
HERE.
For any questions, please contact the skills training team [email protected]
Additional resources for partner organizations:
 MITACS TERMS, CONDITIONS & POLICIES
MITACS TERMS, CONDITIONS & POLICIES
View and download our documents
FAQs
Don’t see an answer to your question? Please contact the team at [email protected] and allow 1-2 business days for us to provide you with an answer.



